What Is Petroleum Jelly and How It’s Used in Industry
Petroleum jelly (also known as petrolatum or Vaseline®) is a semi-solid mixture of refined hydrocarbons derived from petroleum. Thanks to its excellent occlusive properties, stability, and neutral chemistry, it is widely used in skincare, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, mechanical lubrication, electrical insulation, leather conditioning, and corrosion protection; for manufacturers and formulators, partnering with a trusted petroleum jelly supplier helps ensure consistent quality and regulatory compliance across these applications. A comprehensive review in PubMed confirms that refined petroleum jelly is safe for topical use and acts as an effective skin barrier, preventing transepidermal water loss and supporting wound healing.
History of Petroleum Jelly Production and Vaseline Brand
The story begins in the mid-19th century when chemist Robert Chesebrough observed oil workers using a waxy residue from drilling rigs to heal cuts and burns. After refining and purifying this by-product, he patented it in 1872 under the trademark Vaseline®, which soon became synonymous with petroleum jelly worldwide.
Why Modern Petroleum Jelly Factories Are Important
Modern petroleum jelly factories use advanced refining techniques such as hydrotreating, bauxite filtration, and hydrogenation to achieve pharmaceutical- and cosmetic-grade purity.
The global petroleum jelly market was valued at USD 1.37 billion in 2024 (The Business Research Company) and is expected to grow at a 3.9 % CAGR between 2025 and 2035 (Future Market Insights). In the U.S. alone, over-the-counter petroleum jelly products generated $147 million in revenue and 44 million unit sales in 2023 (Statista). This sustained demand makes production facilities strategically important.
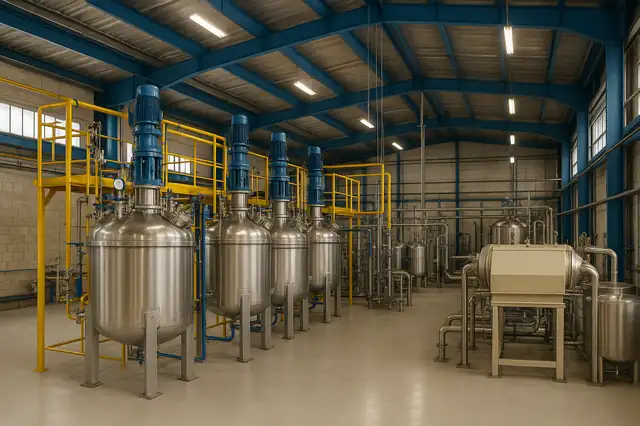

Navid Noor Polymer, a leading petroleum jelly manufacturer, is recognized as one of the largest and most advanced petroleum jelly factories in the region, specializing in the production of high-quality Vaseline (petroleum jelly) for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and industrial applications. With state-of-the-art refining technology, strict adherence to USP/BP/Ph. Eur standards, and a fully GMP-compliant manufacturing process, the company delivers highly purified, safe, and reliable petroleum jelly products to both domestic and international markets. Navid Noor Polymer’s large-scale production capacity and continuous innovation have positioned it as a leading supplier trusted by major brands and global distributors.
How Is Petroleum Jelly Made? Step-by-Step Petroleum Jelly Production
Raw Materials — Crude Oil Fractions, Paraffin Wax, and White Oils
Petroleum jelly manufacturing starts with heavy fractions of crude oil, including paraffin wax, microcrystalline waxes, and white mineral oils. These components provide the semi-solid structure and smooth texture of the final product.
Distillation and Purification in Petroleum Jelly Production
The first major step is vacuum distillation, where crude oil is separated into lighter and heavier fractions. Heavy wax-rich streams are then treated through filtration and adsorption (often using activated bauxite) to remove color, odor, and aromatic impurities.
Hydrogenation and Stabilization of Petroleum Jelly
Hydrogenation introduces hydrogen atoms into the hydrocarbon chains, increasing oxidative stability, removing residual unsaturation, and extending shelf life. This step ensures the jelly remains color-stable and odorless even after long storage.
Filtration and Deodorization in Petroleum Jelly Factories
Following hydrogenation, the product undergoes deep filtration to remove particulates and a deodorization stage to achieve the clean, neutral scent required for medical and cosmetic use.
Cooling, Homogenization, and Packaging Process
The refined material is then cooled under controlled conditions to achieve the desired texture, homogenized for consistency, and filled into drums, pharmaceutical containers, or retail jars in a hygienic packaging area.
Petroleum Jelly Factory Equipment and Production Line
Mixing and Heating Vessels Used in Petroleum Jelly Factories
Factories rely on stainless-steel jacketed vessels with controlled heating and mechanical agitators to melt waxes and mix them evenly with oils.
Filtration Systems and Quality Control Units
Filter presses, bauxite adsorption columns, and fine cartridge filters ensure removal of color bodies, aromatics, and residual solids. Inline sensors monitor temperature, viscosity, and contamination.
Packaging and Storage Facilities in Petroleum Jelly Production
Finished petroleum jelly is filled into sterile, climate-controlled packaging areas. Storage tanks are designed to maintain stable temperature and prevent contamination.
Batch vs Continuous Petroleum Jelly Production Systems
Some factories operate batch processes for flexibility and custom grades; others use continuous systems to maximize throughput and efficiency for large-scale industrial demand.
Petroleum Jelly Production Standards and Regulations
USP, BP, and Ph. Eur Requirements for Petroleum Jelly
Medical and cosmetic petroleum jelly must comply with pharmacopeial standards such as USP (United States Pharmacopeia), BP (British Pharmacopoeia), and Ph. Eur (European Pharmacopoeia). These specify purity, color, melting point, and hydrocarbon composition.
Quality Control Tests in Petroleum Jelly Factories
Factories perform melting point analysis, viscosity measurement, color comparison, odor checks, and microbiological tests on every batch. Trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and mineral oil aromatic hydrocarbons (MOAHs) must remain below strict safety limits.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for Petroleum Jelly Production
Facilities follow GMP / cGMP protocols: documented processes, validated equipment, clean environments, and traceable raw material sourcing — critical for pharmaceutical-grade petrolatum.
Grades of Petroleum Jelly and Their Applications
Pharmaceutical Grade Petroleum Jelly Production
Pharmaceutical petroleum jelly is highly refined, non-comedogenic, and hypoallergenic. It is used in ointments, wound dressings, burn care, and post-surgical skin protection. A review in PubMed confirms its long history of safe medical use.
Cosmetic Grade Petroleum Jelly for Skincare and Beauty
Cosmetic-grade jelly is key in moisturizers, lip balms, slugging routines, makeup removal, and protecting skin during hair dyeing. A histological study showed its strong occlusive performance compared to other emollients.
Industrial Grade Petroleum Jelly for Lubrication and Machinery
Industrial petrolatum serves as a lubricant, rust inhibitor, release agent for molds, and protective coating for metal surfaces. Its stability and cost-effectiveness make it ideal for heavy-duty environments.
Safety and Environmental Impact of Petroleum Jelly Production
Is Petroleum Jelly Safe for Skin and Medical Use?
Refined petroleum jelly meeting pharmacopeial standards is safe for topical use. Concerns about carcinogens relate to unrefined petroleum by-products, not the fully purified product used in cosmetics and medicine.
Environmental Considerations in Petroleum Jelly Factories
Petroleum jelly is typically a by-product of oil refining, meaning its production does not drive additional crude extraction. However, factories are improving energy efficiency, reducing process waste, and adopting cleaner filtration systems.
Sustainable Petroleum Jelly Production Practices
Sustainability efforts include optimized deoiling, non-polar modifier technologies, recyclable packaging, and heat-recovery systems to reduce carbon footprint.
Setting Up a Petroleum Jelly Factory
Cost and Investment Required for Petroleum Jelly Production
Starting a mid-scale petroleum jelly plant requires melting and blending vessels, filtration units, hydrogenation reactors, deodorization systems, and hygienic packaging lines.
Capital investment can range from several hundred thousand to several million USD, depending on capacity and automation level. The global market size (USD 674.35 million for petrolatum in 2024 — Stellar MR) shows profitable potential.
Sourcing Raw Materials and Machinery for a Petroleum Jelly Factory
Reliable suppliers of paraffin wax, microcrystalline wax, and white mineral oils, along with stainless-steel reactors and temperature-controlled mixers, are essential for consistent product quality.
Production Capacity Planning and Factory Layout Tips
Efficient factory layout should separate raw material handling, refining, and packaging zones. Automation and inline quality sensors reduce contamination risk and improve output consistency.
FAQs About Petroleum Jelly Production
How Is Petroleum Jelly Made in Modern Factories?
Petroleum jelly is produced by distilling heavy petroleum fractions, hydrogenating them for stability, filtering to remove impurities, deodorizing, cooling, and packaging under clean conditions.
Petroleum Jelly How Its Made vs Vaseline — What’s the Difference?
Vaseline® is a brand name for high-grade petroleum jelly. Chemically, both are similar, but Vaseline products often meet stricter cosmetic or pharmaceutical purity standards.
Is Petroleum Jelly Production Profitable for Small Factories?
With a global market expected to grow at 3.9 % CAGR through 2035 and strong demand in skincare and medical sectors, small to medium manufacturers can operate profitably with proper quality control and niche positioning.
¿Cómo se hace la vaselina industrial? (Spanish Summary for Global Users)
La vaselina industrial se fabrica a partir de fracciones pesadas del petróleo que se destilan, purifican, hidrogenan y filtran para eliminar impurezas y olores.
Las fábricas modernas usan mezcladores de acero inoxidable, sistemas de filtración con bauxita y estrictos controles de calidad para asegurar un producto seguro y estable.

This is Kamran Malekian working in the petroleum jelly manufacturing industry for Navid Noor Company since 2013 I am eager to make content in this industry and have a good impact on professional users and people using cosmetic and pharmaceutical products.










[…] How is petroleum jelly made? […]